Introduction to Service Data Management
In today’s fast-paced and constantly evolving business environment, accurate and well-organized master data is essential. Service master data management and cleansing are critical to enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring compliance, and enabling data-driven decision-making across industries. Inaccurate or poorly managed service data can result in procurement issues, regulatory non-compliance, and delays, whereas clean, structured data can lead to cost reductions, stronger supplier relationships, and greater agility.
This blog delves into the importance of service master data management, its significance in industrial operations, and the value of maintaining clean, reliable service data. It also highlights how organizations can gain a competitive edge by adopting strong service data management practices.
Before exploring service master data management in depth, it’s important to understand how it differs from material master data management.
While companies have long prioritized master data management for materials, customers, and suppliers, service data often remains overlooked. Despite representing a significant area of spend, service master data management is still relatively new, and many organizations are hesitant to invest in it.
However, like material master data, service master data has grown in both size and complexity over time. Without standardized processes, this data often becomes disorganized, inconsistent, and difficult to manage. As a result, companies face unnecessary challenges and increased costs due to poor-quality service data, such as:
- Absence of standardized data entry protocols
- High levels of duplication
- Lack of visibility across different locations
- Uncontrolled or rogue spending
- Limited ability to reduce procurement costs
Service Master Data Management (SMDM) addresses these issues by cleansing, organizing, and automating service master data to ensure accuracy and visibility across the organization. With a consolidated, de-duplicated, and reliable single source of truth, companies can improve data analysis, reduce costs, and make smarter business decisions.
A robust SMDM solution goes beyond one-time cleansing. It delivers a repeatable, long-term framework by implementing data standards, categorizing and structuring services, standardizing descriptions, and enforcing ongoing governance to maintain data quality and consistency across the enterprise.
Key Differences Between Material Master and Service Master Data Management
In the realm of master data management, Material Master and Service Master Data are two vital yet distinct elements that support efficient business operations. While both are crucial for procurement, inventory control, and overall operational effectiveness, they differ significantly in structure, purpose, and application. Here are the key differences:
Definition and Scope
Material Master Data
Refers to tangible items like raw materials, components, finished products, or spare parts. It contains details such as material type, unit of measure, stock levels, and storage location, with a primary focus on inventory control and supply chain operations.
Service Master Data
Relates to non-physical deliverables like consulting, maintenance, logistics, or IT services. It includes information such as service descriptions, pricing models, service classifications, and vendor details, focusing on the efficient management of intangible resources.
Nature of Data
Material Master Data
Materials are tangible, quantifiable, and come with defined characteristics like size, composition, weight, and shelf life. These measurable attributes make it possible to track and manage materials effectively throughout the supply chain.
Service Master Data
Services are qualitative and not easily quantifiable. They are characterized by descriptive elements like scope, duration, and service level agreements, rather than physical attributes.
Usage in Business Processes
Material Master Data
Materials play a key role in processes such as inventory control, production scheduling, and goods procurement. They are physically stored, monitored, and handled within warehouses or manufacturing sites.
Service Master Data
Enables streamlined procurement of services, oversight of contracts, and assessment of vendor performance. Unlike physical goods, services are delivered either on-site, remotely, or via external providers and are not stored in physical locations.
Classification Standards
Material Master Data
Commonly organized using standardized classification systems like UNSPSC or E-class to ensure consistency and efficiency across supply chain activities.
Service Master Data
Services are often categorized according to international standards such as UNSPSC, aiding in procurement processes and spend analysis.
Complexity of Management
Material Master Data
Material master data is often categorized using internal systems or external standards like UNSPSC and E-class to ensure consistency in supply chain operations. Due to its tangible and repeatable nature, materials are relatively straightforward to manage, with inventory systems and ERP platforms offering robust tools for tracking and control.
Service Master Data
Managing service master data is more complex due to the subjective and customized nature of services. It demands detailed descriptions, strong governance frameworks, and regular updates to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Although material master data is well-defined and supported by traditional ERP systems, Service Master Data Management is often overlooked despite its equal importance to business success. Both Material Master and Service Master Data are essential for business operations, and understanding their differences is key to effective master data management. While Material Master Data focuses on the physical flow of goods, Service Master Data centers on the efficient management of intangible services. This blog will place a greater emphasis on Service Master Data Management, exploring strategies, tools, and best practices that organizations can leverage to effectively handle, track, and optimize service data across various business functions.
What is Service Master Data Management and Why it is required?
Service master data encompasses the essential information about services that a company procures, offers, or manages. This includes service descriptions, pricing details, categorization, vendor or provider information, and relevant industry standards such as UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) and E-class. For example, the service “IT Support” can be assigned the UNSPSC code “81111811 - Technical support or help desk services,” ensuring consistent identification across systems and suppliers. Likewise, “Office Cleaning Services” might correspond to UNSPSC code “76111500 - General building and office cleaning and maintenance services,” enabling more streamlined and accurate procurement.
Without proper classification or linkage to standard codes, services can be miscategorized. For instance, if “IT Support” is mistakenly grouped under a broad category like “Consulting Services,” it can cause procurement inefficiencies and compliance issues. Additionally, such misclassification could lead to financial inaccuracies by misallocating costs, which negatively impacts budgeting and forecasting.
Effective service master data management involves systematically creating, maintaining, and governing this data to keep it accurate, consistent, and current—ultimately enhancing financial control and operational efficiency.
A Comprehensive Guide to Service Master Data Management for Modern Enterprises
Effective Service Master Data Management (MDM) is crucial for businesses aiming to streamline operations, reduce costs, and maintain compliance with industry standards. A well-organized approach to managing service data involves focusing on several key areas:
-
Standardized Classification: Services should be classified using globally recognized standards like UNSPSC to ensure consistency across business units and systems. This standardization reduces inconsistencies caused by different naming conventions and supports smooth integration with enterprise systems such as ERP and procurement platforms. It also enhances spend analysis, compliance, and data transparency.
-
Accurate Data Entry: Ensuring accuracy at the point of data entry is vital to avoid errors that can multiply throughout the system. Mistakes in service data often result in duplicates, flawed reports, and poor decision-making. Implementing validation rules and training employees on best practices helps build a strong foundation for data quality and lowers operational costs.
-
Governance Framework: Establishing a solid governance structure assigns clear accountability, defines ownership, and creates workflows for managing service data. This framework safeguards data Assure by preventing unauthorized changes and aligns data management with overall organizational goals. It also supports compliance and audit readiness.
-
Technology Enablement: Utilizing advanced MDM software is essential to centralize, validate, and monitor service data. Automation features aid in classification, deduplication, and data enrichment, significantly improving accuracy and efficiency. Integration with AI and machine learning technologies further enhances insight generation by detecting patterns and anomalies, helping businesses stay agile and competitive.
-
Regular Data Audits: Conducting periodic audits helps maintain the accuracy, relevance, and alignment of service data with current business requirements. Audits identify and correct inconsistencies, duplicates, and obsolete information. They also reveal opportunities for cost savings through consolidating redundant services or renegotiating contracts while minimizing compliance risks.
-
Interdepartmental Collaboration: Effective service data management depends on collaboration across procurement, finance, operations, and IT teams. Procurement provides vendor-specific insights, finance ensures accurate cost allocation, and IT manages seamless system integrations. This teamwork aligns service data with organizational objectives and promotes consistency across departments.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: Service MDM systems must be scalable to support business growth and flexible enough to adapt to evolving needs. As organizations expand, the number and complexity of services increase, requiring systems capable of handling large datasets and intricate service structures. Flexibility also allows adaptation to new regulations, market shifts, and technological advances.
Key Challenges in Managing Service Data Effectively
Service data management is vital for operational efficiency, especially in industries that depend heavily on outsourced services or complex procurement networks. However, managing service data presents unique challenges. Unlike material data, which involves tangible items, service data is intangible, diverse, and often unstructured. These traits make it more difficult to classify, standardize, and manage effectively. Below, we examine the main challenges organizations encounter when handling service data and the potential impact on their operations.
-
Lack of Standardized Classification
One of the primary challenges in managing service data is the absence of consistent classification standards. Services, unlike materials, are often described differently by various stakeholders, leading to inconsistent entries in service master data.
-
Impact: This inconsistency hampers integration with enterprise systems like ERP and procurement platforms, complicating spend analysis and vendor comparisons.
-
Solution: Adopting globally recognized classification systems, such as UNSPSC, can help ensure uniformity and make data more accessible across departments.
-
Inconsistent and Incomplete Data
Service data often lacks the structured attributes found in material data, making it prone to errors and omissions. For example, incomplete service descriptions or missing pricing details can lead to inefficiencies in procurement and vendor management.
-
Impact: Incomplete data causes delays in service delivery, increases procurement costs, and creates challenges in decision-making.
-
Solution: Implementing data validation processes and mandatory data fields can help maintain data completeness and accuracy.
-
Difficulty in Quantifying Services
Unlike materials, which can be measured and tracked in units, services are qualitative in nature and often lack clear quantifiable metrics. This makes it challenging to assess the value and performance of services.
-
Impact: The inability to quantify services results in poor vendor performance tracking and difficulty in cost allocation.
-
Solution: Defining measurable service-level agreements (SLAs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) can help quantify and evaluate service quality.
-
Decentralized Data Management
Service data is often scattered across various departments, such as procurement, finance, and operations, with no centralized repository.
-
Impact: This decentralization leads to data duplication, discrepancies, and siloed information, undermining collaboration and consistency.
-
Solution: Investing in a centralized master data management (MDM) system allows for better data governance and ensures service data remains consistent and accessible across the organization.
-
High Complexity and Diversity of Services
Services vary significantly across industries and vendors, from one-time consultancy engagements to recurring maintenance contracts. This diversity adds complexity to service master data management.
-
Impact: Managing such varied data without proper categorization leads to inefficiencies in procurement and makes reporting more cumbersome.
-
Solution: Categorizing services into predefined hierarchies and leveraging advanced classification tools can simplify data management.
-
Lack of Ownership and Governance
Without clear accountability, service data management often falls through the cracks. Departments may create duplicate or inconsistent entries due to the lack of defined ownership and governance policies.
-
Impact: Poor governance results in data errors, audit failures, and reduced confidence in service data quality.
-
Solution: Establishing a governance framework that defines roles, responsibilities, and approval workflows ensures accountability and adherence to data quality standards.
-
Limited Use of Technology
Many organizations still rely on manual processes or outdated tools for managing service data, which are neither scalable nor efficient.
-
Impact: Limited technological adoption leads to slow data processing, human errors, and an inability to adapt to changing business needs.
-
Solution: Leveraging advanced MDM platforms equipped with AI and automation capabilities can enhance data accuracy, deduplication, and scalability.
-
Frequent Data Changes and Updates
Service data often requires frequent updates due to changing vendor agreements, pricing structures, or regulatory requirements.
-
Impact: Without proper version control and monitoring mechanisms, these changes can result in outdated or incorrect data being used in critical processes.
-
Solution: Regular data audits and automated update mechanisms help maintain up-to-date and accurate service data.
Key Steps in Service Data Management
Service data management is a crucial component of any organization’s data governance framework. As services play a central role in modern business operations, effective management of service data can drive improved procurement practices, strengthen compliance, and boost operational efficiency. Below are the key steps in the service data management process, spanning from data collection through to validation.
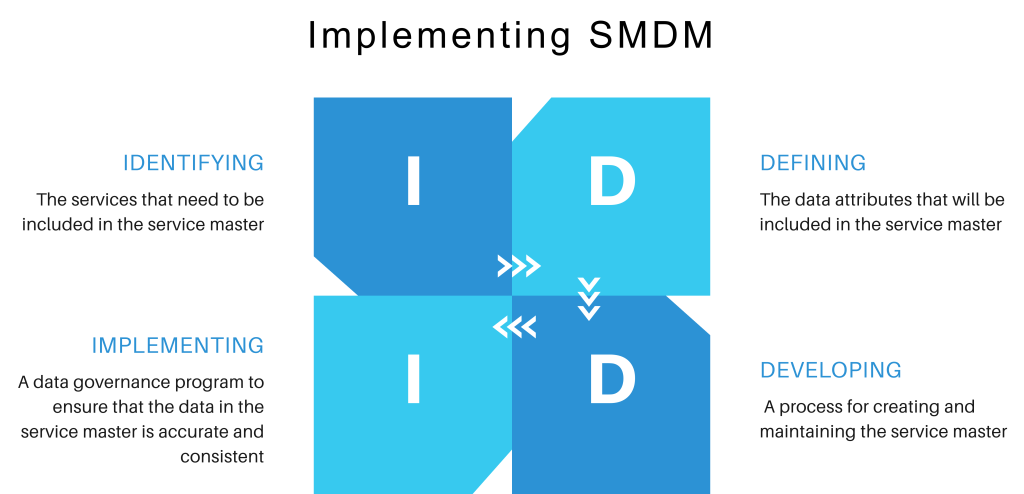
-
Data Collection: Sources of Service Data
The first step in effective service data management is the collection of service-related information. This involves gathering data from multiple internal and external sources to ensure a comprehensive and accurate record of all services provided or received by the organization.
Common sources of service data include:
-
Contracts: Contain detailed descriptions of services, pricing structures, service level agreements (SLAs), and terms and conditions. Contracts serve as a primary reference for data related to the scope, duration, and cost of services.
-
Invoices: Provide critical data on service usage, pricing, discounts, payment terms, and dates of service delivery. They are vital for tracking the financial aspect of service procurement.
-
Procurement Systems: Contain records of service purchases, including vendor information, service specifications, quantities, and payment history. These systems are key sources for tracking ongoing or recurring services.
-
Service Requests and Work Orders: In organizations with maintenance or operations teams, work orders and service requests serve as sources of real-time service data, documenting requests for specific services and their status.
Collecting service data from multiple systems helps create a comprehensive and accurate picture of the services an organization uses, ensuring that the data reflects the latest transactions and agreements.
-
Classification: Grouping Services Using Appropriate Taxonomies
Once service data is collected, the next crucial step is classification—grouping services into categories that can be easily managed, compared, and analysed. Effective classification helps streamline procurement, improve spend analysis, and ensure that services are aligned with business objectives.
Common classification systems include:
-
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code): A global classification standard categorizing services into segments, families, classes, and commodities, ensuring consistency across procurement systems and markets. For example, consulting services could be categorized under the segment “Professional Services,” with further subcategories for specific types of consulting (e.g., IT consulting).
-
E-class: Widely used in Asia, particularly helpful for industries like manufacturing and engineering. It allows for more granular classification of services, emphasizing attributes that define the nature of the service.
We will explore UNSPSC and E-class in greater detail as we progress through this blog.
-
Custom Taxonomies: Some organizations may develop their own custom classification systems based on internal requirements or industry-specific needs.
Proper classification improves visibility and transparency into service-related spending and allows businesses to quickly assess service performance across categories.
-
Validation: Ensuring Service Descriptions, Units of Measure, and Prices Align with Business Requirements
After collecting and classifying the service data, the next step is validation—ensuring that the data aligns with business requirements and is accurate, complete, and up to date. This is crucial for maintaining the Assure of the data and minimizing errors or discrepancies that could impact decision-making.
Key validation activities include:
-
Service Descriptions: Ensuring that service descriptions are accurate, clear, and consistent with internal and vendor-specific documentation. Descriptions should match the agreed scope of work and meet the organization’s quality standards.
-
Units of Measure (UOM): Verifying that the units of measure (e.g., hours, pieces, contracts) are consistent with business standards and appropriate for the type of service provided. For example, if a service is billed by hours, the UOM should clearly reflect this to avoid billing disputes.
-
Pricing and Terms: Ensuring pricing information, payment terms, and discounts are consistent with contracts and agreements. Regular validation of service pricing is especially important in long-term contracts where price adjustments or service additions may occur.
-
Compliance Checks: Ensuring that services comply with industry regulations, internal policies, and quality standards. This is critical in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where non-compliance could lead to legal or financial consequences.
Validating service data is an ongoing process that helps ensure services are provided and paid for correctly, improving financial control and reducing the risk of errors and disputes.
Download Case Study

Elevating Operational Performance with Enhanced Data Quality in Electric Utilities
Leveraging Standards Like UNSPSC and E-class for Service Data
Managing service data effectively is essential for enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring regulatory compliance, and reducing costs. Due to the complexity and variety of service data, organizing, classifying, and standardizing it can be challenging. This is where widely accepted standards such as UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) and E-class become invaluable. These classification frameworks offer a systematic approach to categorizing service data, promoting uniformity across different systems, regions, and industries.
Overview of UNSPSC and E-class
UNSPSC
The UNSPSC is an international classification system created to consistently categorize products and services. It employs a hierarchical coding structure with several levels:
E-Class
E-class is a widely accepted global classification system, especially prevalent in Asia. It facilitates the standardization of product and service data across various industries and platforms. Key features of E-class include:
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code)
UNSPSC is a global classification system designed to uniformly categorize products and services. It employs a hierarchical code structure with multiple levels:
-
Segment: A broad category (e.g., Services).
-
Family: A narrower category within the segment (e.g., Professional Services).
-
Class: A more specific grouping within the family (e.g., Consulting Services).
-
Commodity: The most detailed level (e.g., IT Consulting).
This hierarchical structure allows businesses to drill down into detailed classifications while maintaining a high-level overview. UNSPSC is widely adopted across procurement, spend analysis, and e-commerce platforms.
E-class
E-class is another globally recognized classification system, especially popular in Asia. It facilitates the standardization of product and service data across industries and systems. Key features of E-class include:
- A detailed taxonomy with attributes for describing products and services.
- Support for multiple languages and compliance with international standards.
- Flexibility to map to other standards such as UNSPSC.
Both UNSPSC and E-class are widely used in manufacturing, engineering, and procurement to standardize product and service data effectively.
How UNSPSC and E-class Help in Categorizing and Standardizing Service Data
-
Improved Data Consistency and Accuracy
Implementing standardized classification systems like UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) or E-class ensures consistent data entry across departments, business units, and systems. Without such standards, different teams may use varied terminologies, causing inconsistencies in service descriptions and procurement records. These discrepancies can lead to incorrect data interpretation, flawed spend reports, and inefficiencies in supplier communication. By adopting a structured framework, organizations reduce duplication, minimize manual errors, and enhance overall data quality, ultimately supporting better decision-making and reporting.
-
Enhanced Spend Analysis and Procurement Efficiency
Standardized service data is essential for effective procurement strategies, enabling accurate spend analysis. By categorizing services under specific UNSPSC or E-class codes, organizations can identify cost-saving opportunities and monitor spending trends more effectively.
-
Cost Benchmarking: Assigning standard codes to services such as IT, consulting, or facility management allows companies to compare costs against industry benchmarks and spot overpriced services.
-
Supplier Rationalization: Clear categorization helps analyze the supplier base, consolidate procurement, negotiate better contracts, and secure bulk discounts while improving supplier performance.
-
Fraud Detection: Proper classification aids in uncovering anomalies like duplicate invoices, overbilling, or unnecessary expenses that might be missed in unstructured data.
-
Seamless Integration Across Systems
Enterprise-wide platforms such as ERP, procurement software, and analytics tools require a common language for data exchange. Standardized service classification enables smooth integration, ensuring consistent data flow across procurement, finance, and operations. Benefits include:
-
Automated Workflows: Accurate categorization supports automation in procurement approvals, budgeting, and expense tracking, reducing manual efforts.
-
Interoperability: Standard codes facilitate cross-border transactions by aligning procurement data with international suppliers, minimizing discrepancies.
-
Enhanced Reporting: Aggregating services under standardized categories enables accurate reporting and better visibility into procurement trends and cost allocation.
-
Compliance with Global Standards
Following classification standards like UNSPSC and E-class helps organizations comply with international procurement regulations and reporting requirements, reducing risks related to penalties, contract disputes, and legal issues. Key benefits include:
-
Transparency in Audits: Regulators and auditors can efficiently track and verify procurement activities when services are correctly categorized.
-
Alignment with Tax and Legal Regulations: Many jurisdictions mandate specific classifications for tax reporting and compliance, helping organizations avoid financial risks.
-
Avoidance of Trade Restrictions: Proper classification assists in adhering to trade agreements and prevents procurement-related sanctions or restrictions.
-
Scalability and Flexibility
Both UNSPSC and E-class are designed to support business growth and adaptability. As organizations expand their services, they can seamlessly incorporate new categories without disrupting existing procurement workflows. These classification systems also enable businesses to:
-
Adapt to Market Changes: Update service categories to reflect emerging technologies, industry trends, and evolving business needs.
-
Support Multi-Region Operations: Standardize service procurement across different regions to ensure consistent data entry and reporting.
-
Improve Strategic Decision-Making: Easily analyze service costs, supplier performance, and contract efficiencies through well-structured classifications.
Risks of Incorrect Classification
Inaccurate classification of services can cause serious operational and financial issues, such as:
-
Incorrect Budget Allocation: Misclassified services might be charged to the wrong cost centers, leading to budget overruns or poor financial management.
-
Inaccurate Spend Analysis: Improper categorization can prevent procurement teams from spotting cost-saving opportunities, resulting in inefficient expenditure.
-
Regulatory Non-Compliance: Misclassification may cause errors in tax reporting, potentially resulting in legal penalties and financial losses.
-
Supplier and Contract Mismanagement: Contracts negotiated based on inaccurate service classifications can lead to unfavorable terms or unnecessary costs.
-
Operational Disruptions: Incorrect classifications in automated procurement systems can cause delays in service delivery, invoicing errors, or compliance failures.
Potential Disasters from Poor Classification
Misclassifying services can cause significant business disruptions and financial setbacks. Some of the most severe consequences include:
-
Fraud and Financial Losses: Without accurate classification, companies risk paying for duplicate or nonexistent services, leading to fraud and revenue leakage.
-
Contractual and Legal Disputes: Misclassification may cause contracts to misalign with service expectations, resulting in disputes, litigation, or contract terminations.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Incorrectly categorized services might lead procurement teams to engage the wrong suppliers, causing delays, service failures, or compromised quality.
-
Reputational Damage: Regulatory breaches, inefficiencies, and poor supplier management arising from misclassification can damage an organization’s reputation and erode stakeholder trust.
Implementing UNSPSC and E-class classification systems enhances data accuracy, boosts procurement efficiency, ensures compliance, and supports business growth. However, organizations must invest in proper implementation, training, and regular audits to mitigate risks related to misclassification. A robust classification framework empowers businesses to make informed procurement decisions, optimize spending, and maintain operational excellence in today’s complex global marketplace.
Practical Examples: Mapping Services to UNSPSC Codes for Global Standardization
Automated, Software-based Approach
An IT consulting firm can utilize UNSPSC to standardize its service offerings as follows:
-
Segment: 80000000 (Management and Business Professionals and Administrative Services)
-
Family: 80100000 (Management advisory services)
-
Class: 80101500 (Business and corporate management consultation services)
-
Commodity: 80101507 (Information technology consultation services)
This classification ensures that all IT consulting services are consistently categorized, facilitating precise spend analysis, vendor comparison, and improved procurement efficiency.
Example 2: Water Leakage Maintenance Services
A corporate firm seeking maintenance services can map them using UNSPSC as follows:
-
Segment: 70000000 (Building and Facility Construction and Maintenance Services)
-
Family: 72100000 (Building and facility maintenance and repair services)
-
Class: 72101500 (Building maintenance and repair services)
-
Commodity: 72101510 (Plumbing system maintenance or repair)
Standardizing maintenance services using UNSPSC promotes clear procurement contracts, effective vendor management, and adherence to industry regulations.
Example 3: E-class for Engineering Services
Using E-class, an engineering company can specify detailed service attributes for precise classification:
E-class codes:
-
15220100 Centrifugal pump (maintenance)
-
15220101 Centrifugal pump (inspection)
-
15220102 Centrifugal pump (servicing)
-
15220103 Centrifugal pump (repair)
-
15220104 Centrifugal pump (improvement)
This categorization enables detailed reporting and seamless integration with other standards, ensuring data accuracy across platforms.
UNSPSC and E-class provide robust frameworks for categorizing and standardizing service data, helping businesses address challenges such as inconsistency, inefficiency, and lack of global alignment. By adopting these standards, organizations can improve data quality, streamline procurement processes, and gain valuable insights through enhanced analytics.
In today’s interconnected business environment, embracing comprehensive classification standards like UNSPSC and E-class is not only a best practice but a strategic imperative for achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Future Trends in Service Data Management
As businesses evolve in an increasingly digital world, service data management is transforming through emerging technologies and automation. Efficiently managing, standardizing, and validating service data is becoming essential for organizations aiming to optimize procurement, enhance compliance, and improve decision-making. Below are two key trends shaping the future of service data management.
-
Adoption of AI for Service Data Standardization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how organizations classify, validate, and manage service data. AI-driven automation helps overcome common challenges such as inconsistent service descriptions, duplicate records, and manual classification errors.
Key Benefits of AI in Service Data Management:
-
Automated Classification: AI algorithms map service descriptions to standardized taxonomies like UNSPSC and E-class, ensuring consistency across systems.
-
Duplicate Detection & Data Cleansing: Machine learning models identify redundant or conflicting entries and suggest corrections, resulting in higher data accuracy and reduced procurement inefficiencies.
-
Context-Aware Data Enrichment: AI analyzes historical service transactions and recommends additional metadata, such as pricing benchmarks or vendor ratings, to support better decision-making.
For example, AI-powered tools can automatically classify a consulting service under UNSPSC Code 80101500 (Business and Corporate Management Consultation Services), minimizing manual effort and improving procurement transparency.
-
Real-Time Data Updates and Validation in the Cloud
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based procurement and ERP systems, real-time service data management becomes critical. Cloud platforms facilitate seamless data synchronization across departments, ensuring consistent and up-to-date service records.
Major Benefits of Managing Service Data in the Cloud
-
Real-Time Data Updates: Modifications to service details, pricing, and contracts are instantly reflected across all platforms, minimizing errors and ensuring alignment.
-
Automated Data Verification: Cloud solutions connect with external sources and AI-powered validation tools to identify discrepancies, missing information, or incorrect categorizations.
-
Scalability and Adaptability: Cloud systems efficiently handle extensive service data without losing performance, making them suitable for expanding businesses with growing service catalogs.
For instance, a multinational company utilizing a cloud-based Master Data Management (MDM) system can update service pricing across its various locations instantly, ensuring compliance and improving the accuracy of financial planning.
Advantages of Implementing a Services Master:
-
A Unified Central Data Source
An integrated Services Master Data Management (SMDM) platform stores clean, standardized master data in one centralized cloud location, enabling better collaboration across sites and real-time access to updates.
-
Consistent and Structured Descriptions
An advanced services master guarantees company-wide consistency by providing reliable, well-structured service descriptions aligned with global standards like UNSPSC.
-
Enhanced Processes and Performance
Centralized, validated data empowers businesses to analyze performance, make data-driven decisions, remove duplicates, and maintain on-time service routines. Automation helps eliminate delays, streamlining workflows and boosting ERP efficiency.
-
Robust Search Functionality
With features such as keyword searches and category filters, users can quickly locate services by keyword, category, or attributes, enhancing transparency, reducing redundant purchases, and offering detailed views of the services database.
-
Stronger Data Security
SMDM platforms provide enhanced security through role-based user access, authentication, and detailed audit logs. Unauthorized actions are automatically detected, limiting security breaches and improving accountability.
The rise of digital transformation and Industry 4.0 underscores the importance of high-quality data. Since data drives strategic decisions, operational improvements, productivity gains, and cost savings, adopting a cleansed and standardized services master delivers significant advantages. Embrace services master data management early to stay ahead of the competition!
Conclusion
Effective service master data management is vital for today’s businesses, helping organizations maintain data consistency, meet regulatory requirements, and enhance operational performance. By adopting standardized classification frameworks (UNSPSC, E-class), utilizing AI-powered automation, and implementing cloud-based MDM platforms, companies can greatly boost procurement efficiency, reduce costs, and increase strategic flexibility.
Poor management of service master data can result in serious issues such as procurement delays, inaccurate financial reporting, compliance violations, and lost opportunities for savings. Therefore, establishing strong standardization and governance practices is crucial to safeguard data accuracy and reliability.
How Moresco Can Help
Moresco, a pioneer in Master Data Management solutions, provides robust tools such as PureData and Assure to assist organizations in managing and refining their service master data. These solutions offer:
-
Automated Data Harmonization: Standardizing service descriptions, classifications, and attributes to ensure data consistency.
-
Data Cleansing & Enrichment: Detecting duplicates, correcting inaccuracies, and supplementing service data with missing details.
-
AI-Driven Classification: Utilizing AI to automatically align services with global standards such as UNSPSC and E-class.
-
Seamless Integration: Facilitating real-time synchronization of data across ERP, procurement, and analytics systems.
-
Governance & Compliance Support: Establishing workflows that uphold data Assure and adhere to industry regulations.
By leveraging Moresco’ advanced technology, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies, streamline procurement operations, and improve overall data quality—transforming service master data management from a challenge into a strategic advantage. Investing in the right tools and practices ensures companies stay competitive and well-prepared to handle the complexities of modern procurement and service management.

