Streamlined Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) Cataloguing and Category Management are key to improving industrial and operational workflows. These practices involve organizing, classifying, and managing MRO assets—like machinery, tools, spare parts, safety equipment, and consumables—to enhance inventory oversight, boost procurement efficiency, and control costs.
By applying robust classification frameworks and adhering to standardized protocols, organizations can better track items, eliminate duplication, improve data reliability, and make smarter sourcing decisions. Implementing MRO Data Governance ensures that catalogued data remains accurate, well-classified, and compliant with both internal policies and industry regulations, ultimately improving procurement and operational effectiveness. Effective MRO Category Management goes further by analyzing spend categories, strengthening supplier relationships, and applying best procurement practices to maximize value.
This guide highlights critical principles, classification methods, advantages, standards, and audit techniques necessary for optimizing MRO. Whether your focus is on increasing efficiency, lowering costs, maintaining compliance, or simplifying procurement, this blog offers valuable insights and proven strategies to enhance your MRO data management processes.
MRO Category Management
MRO category management is a strategic approach to overseeing the procurement and supply chain of MRO products and services. It involves segmenting MRO spend into distinct categories, optimizing supplier partnerships, and reducing costs—all while ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Fundamentally, MRO category management provides strategic control over procurement, inventory, and supply chain processes related to MRO items, ensuring alignment with broader business goals. This includes optimizing MRO inventory levels, refining procurement workflows, strengthening supplier relationships, and using data-driven insights to cut costs and boost operational efficiency.
MRO items typically include:
- Maintenance materials including lubricants, belts, bearings, and fasteners.
- Repair components such as spare parts, motors, pumps, and seals.
- Operational supplies including safety gear, cleaning materials, and hand tools.
MRO Category Management: Step-by-Step Process
MRO Category Management is a structured approach to efficiently oversee maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) spare parts, consumables, and maintenance materials. It helps control costs, optimize supplier relationships, and ensure uninterrupted operations by systematically managing MRO procurement, inventory, and usage.
Below is a step-by-step process outlining how organizations can streamline their MRO category management.
Step 1: Spend Analysis & Data Collection:
The first step in MRO Category Management involves conducting a thorough spend analysis to understand procurement trends, identify inefficiencies, and reveal potential cost-saving opportunities. Organizations should collect historical purchasing data from ERP systems, CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems), and supplier invoices to gain insight into their spending patterns.
MRO expenditures need to be categorized into groups such as spare parts (bearings, belts, gaskets), consumables (lubricants, adhesives, gloves), and tools & equipment (drills, calibration instruments, wrenches). A detailed examination of this data helps detect duplicate purchases, price inconsistencies, and supplier dependencies. Evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) allows companies to consider not only the unit price but also storage, handling, obsolescence, and logistics costs.
For instance, analyzing bearing purchases might reveal that the same 6203 ball bearing is sourced from multiple suppliers at different prices, leading to unnecessary expenditure.
Step 2: Supplier Segmentation & Consolidation:
MRO procurement often involves a large number of suppliers, leading to fragmented purchasing, inconsistent pricing, and complex supplier management. Categorizing suppliers based on factors such as cost, reliability, and service quality helps simplify vendor management. Suppliers are classified into preferred suppliers (approved vendors offering competitive prices), critical suppliers (specialized providers for unique MRO parts), and transactional suppliers (used for low-value, infrequent purchases).
Consolidating suppliers plays a key role in reducing procurement complexity. Instead of sourcing hydraulic seals from five different vendors, companies can streamline purchases by partnering with one or two top suppliers to secure better volume discounts and ensure standardization. Competitive bidding for frequent purchases like gaskets, fasteners, and lubricants via long-term contracts helps secure more favorable pricing and service agreements. Continuous monitoring of supplier performance ensures timely deliveries and high-quality service.
Step 3: Demand Forecasting & Standardization:
Demand forecasting is a crucial aspect of MRO management, allowing organizations to optimize inventory levels by predicting future needs based on historical usage patterns. Utilizing predictive analytics, companies can anticipate demand for frequently used items such as filters, lubricants, and fasteners to prevent stock shortages.
Standardization plays a vital role in avoiding duplicate purchases and excessive SKU proliferation. Adopting consistent naming standards—such as UNSPSC or eCl@ss classifications—helps ensure that identical parts are not ordered under different names. Reducing unnecessary variations in spare parts is another key strategy.
For instance, instead of stocking multiple versions of M8 bolts with slight specification differences, companies can standardize on a single specification across all departments, leading to better availability and cost control.
Step 4: Strategic Sourcing & Procurement Optimization:
Optimizing procurement allows companies to reduce costs and enhance efficiency. Employing competitive bidding and reverse auctions for high-value items such as industrial lubricants, machine filters, and electrical components helps secure the best pricing. Additionally, partnering with group purchasing organizations (GPOs) can lead to better deals on commonly used consumables like welding rods, electrical tape, and safety glasses.
E-procurement platforms streamline the buying process by automating purchase requests, approvals, and supplier management. Furthermore, optimizing order schedules can help reduce excess freight and handling fees.
For example, instead of placing weekly last-minute orders for machine belts, companies can organize bulk purchases quarterly, thereby lowering procurement effort and shipping expenses.
Step 5: Inventory Optimization & Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI):
Efficient inventory management is crucial for maintaining optimal stock levels while minimizing excess inventory costs. Companies can adopt Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory methods for frequently used MRO items like nuts, bolts, and gaskets to ensure they carry only what is necessary.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) programs allow suppliers to monitor stock levels and automatically replenish critical parts, reducing the risk of shortages. Inventory classification methods such as ABC analysis help prioritize inventory management efforts effectively.
-
A-class items (high-value, mission-critical spares such as gearboxes and pumps) require close oversight and low stock levels to prevent capital from being tied up unnecessarily.
-
B-class items (moderately priced components like filters and fuses) need balanced inventory levels to optimize both cost and availability.
-
C-class items (low-cost, high-usage commodities such as fasteners and cable ties) can be purchased in bulk as they have minimal impact on total expenditure.
Technologies such as RFID tracking and barcode scanning provide real-time visibility into inventory, helping to reduce losses and avoid unnecessary stock.
For instance, instead of stocking 30 different sizes of hydraulic fittings, a VMI agreement can ensure automatic replenishment of only the most commonly used sizes, reducing excess inventory and storage costs.
Step 6: Performance Monitoring & Continuous Improvement:
MRO Category Management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and enhancement. Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, supplier lead times, and cost savings achieved through standardization helps measure the effectiveness of procurement activities.
Conducting quarterly supplier audits allows businesses to ensure compliance with contract terms and identify opportunities for improvement. Predictive analytics can also help anticipate seasonal demand changes, enabling proactive sourcing strategies.
Regularly updating MRO procurement policies and procedures ensures alignment with industry best practices.
For instance, if electric motor bearings frequently run out of stock, revising reorder points based on past demand trends can prevent future shortages and minimize downtime.
The Strategic Importance of MRO Category Management
Effective management of MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) categories is fundamental to boosting efficiency, cutting expenses, and ensuring smooth operations. While it may not always get the spotlight, a strategic approach to MRO management is important for these key reasons:
-
Cost Optimization
MRO expenses often represent a significant part of operational budgets. Inefficient and fragmented procurement processes can lead to overspending and missed opportunities for savings. By implementing category management, organizations can analyze spending patterns, consolidate suppliers, and negotiate better contracts, ensuring each dollar spent delivers maximum value while minimizing waste.
-
Ensuring Operational Continuity
Supply shortages of critical MRO items can disrupt productivity and impact revenue. Strategic MRO management guarantees the availability of essential supplies while avoiding excessive inventory that ties up working capital. Maintaining the right inventory balance reduces downtime, improves cash flow, and supports smooth operations.
-
Enhanced Strategic Sourcing
Working closely with dependable suppliers through a category-focused strategy ensures timely delivery of quality materials. This not only prevents operational interruptions but also strengthens supplier partnerships, fostering long-term value and innovation.
-
Compliance and Standardization
Standardizing MRO items and adhering to regulatory requirements are crucial for operational consistency and efficiency. Strategic MRO management aligns with company policies and industry standards, mitigating risks and enhancing reliability.
Far from being a mere support function, MRO category management is a strategic driver of business performance and sustainability. Organizations that embrace a structured MRO approach stand to gain substantial benefits—from cost control to stronger operational resilience.
Key Components of Effective MRO Category Management
An organized and strategic approach to MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) category management involves key elements that together improve the efficiency and effectiveness of managing this vital area of expenditure. These components include:
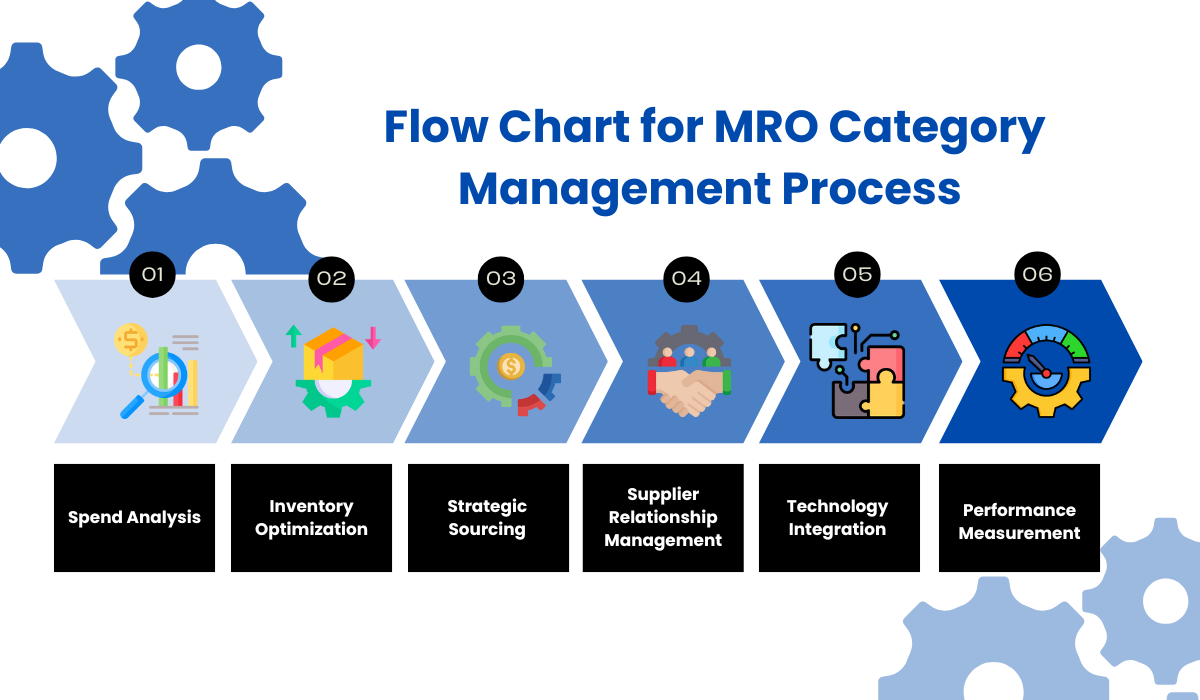
-
Spend Analysis: Conducting a thorough spend analysis is fundamental to uncovering cost drivers, inefficiencies, and improvement opportunities. Gaining detailed insights into MRO expenditures allows organizations to implement strategic actions like supplier consolidation, improved inventory management, and optimized sourcing strategies, driving cost savings and value creation.
-
Inventory Optimization: Effective management of MRO categories ensures critical items are readily available while minimizing excess inventory costs. Methods such as Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory, Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI), and demand planning help reduce waste, lower carrying costs, and boost operational flexibility.
-
Strategic Sourcing: Partnering with suppliers who offer the best balance of cost, quality, and reliability is crucial. Utilizing data analytics facilitates strong contract negotiations, volume discounts, and enhanced supplier partnerships, leading to cost savings and increased supply chain resilience.
-
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): Supplier Data Management plays a central role in fostering collaborative relationships and long-term value. Engaging suppliers in innovation and performance improvement initiatives ensures access to advanced products and technologies while maintaining consistent service levels and flexibility to adapt to changing business needs.
-
Technology Integration: Leveraging modern tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and spend analytics platforms streamlines MRO category management. Predictive analytics enhance demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and proactive decision-making, reducing disruptions and inefficiencies.
-
Performance Measurement: Tracking the effectiveness of MRO category management initiatives involves defining and monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Metrics such as cost savings, inventory turnover, supplier performance, and order cycle times help drive continuous improvement and ensure alignment with business goals.
By combining these elements, organizations can realize substantial cost savings, strengthen supplier partnerships, and streamline MRO operations, ultimately boosting overall business performance.
Best Practices for MRO Category Management
To optimize MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) category management, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
-
Segment MRO Spend
Break down MRO expenditures into distinct categories such as consumables, spare parts, and safety equipment. This segmentation enables tailored strategies for each category, simplifying management while maximizing the impact of cost-saving and operational improvements. -
Leverage Data Analytics
Use data analytics to inform decision-making. Analyzing past spend and usage trends helps uncover inefficiencies, identify savings opportunities, and prioritize high-impact initiatives. A data-driven approach ensures better resource allocation and strategic focus. -
Consolidate Suppliers
Streamline the supplier base to reduce complexity, strengthen relationships, and often secure better pricing and service. Consolidation also lowers administrative burden, improves supply chain efficiency, and ensures better compliance with procurement policies. -
Standardize Materials and Processes
Minimize variability by standardizing materials and processes, simplifying procurement and inventory management, and maintaining consistent quality and performance. Standardization also facilitates bulk purchasing, delivering cost and operational efficiencies. -
Integrate Technology Solutions
Invest in advanced technology such as procurement automation, inventory management systems, and predictive analytics. These tools enhance visibility, improve tracking, and support proactive decision-making across MRO operations. -
Commit to Continuous Improvement
Understand that effective MRO management is an ongoing journey. Regularly evaluate performance metrics, review inventory and supplier effectiveness, and gather stakeholder feedback to stay aligned with evolving business objectives. Fostering a culture of continuous improvement ensures long-term success and agility.
MRO Cataloguing - Classification, Benefits, Conventions & Auditing Procedures
MRO Cataloguing is the organized and systematic approach to classifying and maintaining a comprehensive record of Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) items. It plays a crucial role in MRO Category Management by enabling efficient sourcing and inventory management. These items are vital for the continuous operation, Flowkeep, and repair of industrial machinery, equipment, and facilities. The cataloguing process involves developing a standardized database that delivers accurate and current information about all parts, tools, consumables, and equipment necessary to support optimal operational performance across various industries.
Improved understanding of MRO flow includes:
Classification of Frameworks
UNSPSC and eCl@ss are two globally recognized standards commonly used for categorizing MRO items.
-
UNSPSC is a hierarchical classification framework that organizes products and services into four distinct levels, ranging from broad categories to highly specific items.
-
eCl@ss offers a classification hierarchy enriched with detailed attributes for each product, enabling more precise product specifications.
Example: eCl@ss code for a Spatula Spoon is (32-03-13-04).
These standards ensure uniform classification of items, which streamlines the processes of searching, ordering, and tracking parts across multiple suppliers and systems.
Data Attributes
Creating an efficient MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) catalog requires detailed data attributes for every item. These attributes are crucial for easy identification, tracking, and ordering of MRO parts. Common key data attributes found in MRO catalog records include:
Example of Data Attributes:
| Item | Data Attributes | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Pumps |
– Type: Centrifugal, Positive
Displacement, Diaphragm – Material: Cast Iron, Stainless Steel – Flow Rate: 50 GPM – Pressure: 10 bar – Size: DN50 – Power: 5 HP, 10 HP – Connection Type: Threaded – Seal Type: Mechanical Seal – Manufacturer: XYZ Pumps Ltd. – Model Number: ABC123 |
Type helps choose the right
pump for the application. – Material and seal type specify durability and compatibility with liquids. – Flow rate and pressure ensure the pump can handle required conditions. – Power is necessary for matching energy requirements. – Manufacturer and model number aid in identifying replacement parts. |
| Valves |
– Valve Type: Gate, Ball,
Check, Globe, Butterfly – Material: Brass, Steel, PVC – Pressure Rating: 150 psi, 300 psi – Size: DN40, DN80 – Flow Direction: Bi-directional, Uni-directional – Actuation: Manual, Electric, Pneumatic – Temperature Rating: -10°C to 20°C – End Connection Type: Flanged, Threaded – Manufacturer: ABC Valves Co. – Model Number: VAL123 |
– Valve type is crucial for
determining functionality (e.g., shut-off,
flow control). – Pressure rating ensures the valve can withstand operational pressures. – Actuation and flow direction specify control method and system configuration. – Temperature rating ensures compatibility with operating conditions. – Size and connection type ensure compatibility with associated pipe systems. |
Importance of Taxonomies
A taxonomy is a structured classification system used to organize MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) data into various categories and subcategories. This approach enhances searchability, minimizes errors, and streamlines the procurement process.
Example: An effective taxonomy for a bearing might look like this:
Mechanical Power Transmission > Bearings > Ball Bearings > Deep Groove Ball Bearings
-
Group: Mechanical Power Transmission
-
Category: Bearings
-
Subcategory: Ball Bearings
Specific Type: Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Benefits of Accurate MRO Cataloging:
Proper MRO cataloguing offers several advantages for businesses:
-
Reduced Duplicate Inventory: Prevents the unnecessary stocking of identical items by identifying duplicates.
-
Streamlined Procurement: Enables purchasing teams to easily find and order parts with accurate specifications.
-
Improved Maintenance Planning: Helps maintenance teams schedule tasks more efficiently by ensuring required parts are in stock.
Example: A manufacturing plant regularly ordered spare parts for a pump, only to discover they were accumulating excess inventory due to an outdated catalogue. After reorganizing the catalogue, they maintained only the essential stock, reducing overhead and eliminating surplus.
Core Issues in Material Master Data
At the center of the diagram above are five common data quality issues that impact MRO operations:
- Inaccurate: Data that contains errors, leading to mistakes in operations or procurement.
- Inadequate: Records lacking sufficient detail, resulting in confusion or inefficiencies.
- Inconsistent: Differences in formatting or naming conventions across data entries.
- Illogical: Information that is unreasonable or fails to meet logical validation.
- Missing: Critical information is absent, creating gaps that reduce data usability.
Key Data Elements Impacted
These data quality issues directly impact several critical data elements, as shown on the right:
-
Part Numbers: Unique identifiers used to track and manage items effectively.
-
Vendor Names: Accurate supplier information, essential for smooth procurement processes.
-
Descriptions: Clear and detailed item descriptions that help avoid ambiguity or errors.
-
Classifications: Proper categorization of materials using industry standards like UNSPSC or eCl@ss, aiding in efficient organization and reporting.
-
PO Text Data: Information included in purchase orders, critical for accurate communication with suppliers.
Impact on inventory Management
Effective MRO cataloging plays a key role in inventory management by enabling accurate tracking of parts and ensuring obsolete items are regularly identified and removed.
Example:
A warehouse previously struggled with excess
inventory of outdated filters due to poor
categorization. After introducing a robust
cataloging system, they gained visibility into the
lifecycle of each filter. This allowed them to
reduce unnecessary stock and free up valuable
storage space.
Cataloging Conventions
Maintaining consistency in naming conventions and abbreviations ensures clarity across systems and teams. Standardized naming helps different departments communicate effectively and allows systems to operate seamlessly together.
Example:
Technical Specifications:
-
Include technical details like material, size, temperature, or pressure rating directly in the catalog entry.
Example: “O-Ring, 1” ID, Buna-N, 200 PSI” -
Avoid vague names like “Large Pump.” Instead, use standardized descriptions such as:
“Centrifugal Pump – 10HP – 415V – 50Hz” -
Standardized naming ensures clarity and consistency across systems and teams.
Auditing and Validation
Conducting regular audits is crucial to maintaining an accurate and up-to-date catalog. These processes help identify errors such as duplicate entries, outdated items, or incorrect information.
-
Periodic Data Validation
-
Ensure No Duplicates: Regularly scan the catalog for duplicate entries to avoid confusion and maintain data Assure.
-
Obsolete Items Identification: Flag and remove outdated or discontinued parts to prevent unnecessary purchases.
-
-
Data Enrichment
-
Supplier Details Verification: Ensure all supplier information, including part numbers and contact details, is accurate and current.
-
Cross-Verification with Manufacturer Specifications: Validate item details against official manufacturer data for accuracy.
-
-
Compliance Checks
-
Adherence to Industry Standards: Verify that items comply with applicable standards (e.g., ISO).
-
Alignment with Organizational Policies: Confirm catalog entries align with internal safety, quality, and procurement policies.
-
-
Regular Audits of Stock Levels
-
Minimize Overstock: Audit inventory to identify excess stock and free up storage space.
-
Monitor Stockouts: Track low inventory levels to prevent shortages and maintain continuity.
-
-
Automated Systems Integration
-
Utilize Inventory Management Software: Implement tools for real-time tracking of stock, usage, and purchase history.
-
Automated Alerts for Expiry Dates: Set up alerts for approaching end-of-life items to enable timely actions.
-
-
Monthly Audits
-
Review Audit Results: Analyze audit reports to drive improvements in catalog accuracy and inventory control.
-
Adjustments Based on Findings: Update catalog entries and processes based on audit discrepancies.
-
Automation in Cataloging
AI and Machine Learning technologies can significantly enhance MRO cataloging by automating classification, data enrichment, and inventory synchronization.
-
Real-time Data Integration
-
Sync with Inventory Systems: Automatically update catalog entries with real-time data such as stock levels, usage trends, and order history.
-
Link to Supplier Databases: Integrate with supplier systems to auto-update part numbers, pricing, and lead times—reducing manual data entry errors.
-
-
Automated Classification and Tagging
-
AI-Based Categorization: Use machine learning algorithms to classify items based on attributes such as type, size, material, or function.
-
Auto-Enrichment: Leverage AI to pull detailed attribute data from manufacturer or supplier websites to ensure completeness.
-
Automatic Tagging: Apply metadata tags to catalog entries for enhanced searchability and traceability.
-
-
Predictive Ordering and Restocking
-
Stock Monitoring: Use predictive analytics to track stock levels and anticipate demand, triggering automatic reorders.
-
Reduce Stockouts and Overstocking: Receive automated alerts to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding shortages and excess.
-
-
Automated Expiry Date Tracking
-
Real-time Alerts: Get notified when items are nearing expiration (e.g., filters, perishable parts) to allow proactive action.
-
Expiry Integration: Connect expiration tracking with inventory software to auto-adjust stock levels and flag items for replacement.
-
-
Workflow Automation for Catalog Updates
-
Automated Audit Trails: Log every catalog change automatically to maintain accountability and transparency.
-
Catalog Updates via Automation: Apply audit findings to the catalog automatically to keep data current and accurate.
-
-
User-Friendly Interfaces for Automation
-
Dashboard Integration: Provide users with a real-time view of catalog status, automated actions, and manual override options.
-
Automated Reporting: Generate reports on stock levels, usage trends, and order patterns for simplified decision-making.
-
Vendor Collaboration
Collaborating closely with suppliers is essential for maintaining an accurate and up-to-date MRO catalog. Vendors often provide the latest part specifications, pricing updates, and compliance documentation.
-
Enhanced Communication
-
Regular Meetings: Schedule periodic meetings with suppliers to discuss product updates, pricing changes, and catalog synchronization.
-
Information Sharing: Exchange data on inventory levels, usage trends, and lead times to improve procurement alignment.
-
-
Joint Data Management
-
Integrated Systems: Work together on data integration to enable real-time access to vendor catalogs and shared inventory data.
-
Standardized Item Descriptions: Collaborate on consistent naming conventions, codes, and specifications to reduce errors in ordering.
-
-
Streamlined Ordering Processes
-
Automated Purchase Orders: Use automated systems to trigger POs based on stock thresholds, minimizing delays and manual effort.
-
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): Allow vendors to manage inventory replenishment based on agreed parameters, reducing excess stock and improving availability.
-
-
Collaboration on Inventory Forecasting
-
Demand Forecasting Tools: Utilize shared forecasting tools to predict demand, enabling vendors to plan production and deliveries accordingly.
-
Joint Usage Analysis: Review historical consumption data together to plan for seasonal spikes or bulk purchase opportunities.
-
-
Quality Control and Compliance
-
Joint Audits: Perform collaborative audits to ensure products meet quality specifications and regulatory requirements.
-
Compliance Data Sharing: Exchange certificates, quality reports, and regulatory documents to maintain catalog Assure and meet compliance standards.
-
To gain a better understanding, feel free to watch the video that offers an in-depth overview of our platform.
Integration with ERP Systems
Connecting MRO catalogs with ERP and EAM systems enhances operational efficiency by synchronizing inventory and procurement data across departments.
-
Centralized Data Management
-
Unified Catalog Access: Integrating with ERP systems creates a centralized MRO item repository accessible organization-wide, ensuring data consistency.
-
Real-time Updates: Catalog data is synchronized instantly between MRO and ERP systems, minimizing discrepancies.
-
-
Improved Procurement Process
-
Automated Purchase Orders: Enables automatic generation of purchase orders in the ERP system based on catalog information, streamlining procurement.
-
Enhanced Order Tracking: Provides visibility into order status, allowing procurement teams to monitor progress and address issues promptly.
-
-
Efficient Inventory Management
-
Real-time Stock Levels: Integrates with ERP inventory modules to provide up-to-date stock levels, ensuring accurate tracking and reducing stockouts.
-
Automated Replenishment: Automatically triggers replenishment orders when inventory falls below set thresholds, minimizing overstock and shortages.
-
-
Standardized Item Descriptions
-
Consistency Across Systems: Maintains uniform item descriptions, codes, and specifications between the MRO catalog and ERP, reducing confusion and errors.
-
Eliminates Data Silos: Breaks down departmental silos by offering a unified item view, improving decision-making and operational flow.
-
-
Enhanced Supplier Management
-
Access to Supplier Information: Integrates supplier details such as part numbers, pricing, and lead times into the ERP system, empowering quicker, informed procurement decisions.
-
Automated Vendor Selection: Facilitates vendor selection within the ERP based on criteria like lead times, costs, and compliance.
-
Example:
When an MRO catalog
is integrated with an ERP platform like SAP,
inventory levels update automatically, ensuring
stock aligns with actual inventory. This reduces
errors and delivers real-time data to maintenance
teams.
Lifecycle Management of Items
Catalog items must be regularly reviewed, updated, or deactivated to accurately represent their current lifecycle status (e.g., new, obsolete).
Example: Control Valve Spare Parts
-
Actuator Section: Includes components such as the Rain Cap (1), Eye Bolt (2), Diaphragm (1), Spring (1), Actuator Stem (1), and Diaphragm Case (2). These parts are responsible for moving the valve stem to control the valve’s position.
-
Body Section: Comprises the Scale Plate (1), Stem Connector (1), Yoke (1), Packing Flange (1), Packing Follower (1), Yoke Clamping Nut (2), Gland Packing (1), Valve Stem (1), and Bonnet (1), providing the valve’s structure, sealing, and movement transfer.
-
Trim Section: Contains the Stud Bolts and Nuts (4), Gasket (1), Guide Ring (1), Guide Bushing (1), Valve Plug (1), Seat Ring (1), and Valve Body (1), which are essential for flow control and sealing.
-
Monitoring Item Lifecycle Stages
-
Initial Registration: Ensure each item is accurately cataloged with a unique ID, detailed description, and specifications from the outset.
-
Performance Tracking: Continuously assess the condition of items in use, including wear, frequency of use, and maintenance requirements.
-
-
Managing Expiry Dates
-
Automated Notifications: Configure alerts for items approaching the end of their lifecycle (such as filters or lubricants) to proactively manage inventory and usage.
-
Planned Replacements: Schedule timely replacements for items reaching the end of their lifecycle to avoid operational interruptions.
-
-
Analyzing Historical Data
-
Usage Trends: Examine past data to identify usage patterns, enabling better stock management and reorder decisions.
-
Cost Evaluation: Assess maintenance and replacement expenses to optimize procurement and Flowkeep strategies.
-
-
Monitoring Item Condition
-
Routine Inspections: Conduct regular checks to evaluate the condition of items (e.g., machinery parts, filters) and ensure they meet performance standards.
-
Condition-Based Maintenance: Employ maintenance approaches based on real-time performance data of items.
-
-
Updating Compliance Information
-
Periodic Reviews: Regularly update compliance data for cataloged items to ensure adherence to safety, quality, and regulatory standards.
-
Alert Systems: Implement notifications for upcoming recertifications or required compliance documentation updates.
-
-
Continuous Improvement Feedback Loop
-
User Feedback System: Create a mechanism for users to provide feedback on item performance, aiding in catalog refinement.
-
Ongoing Enhancements: Regularly analyze feedback and performance metrics to update and improve the catalog’s accuracy and relevance.
-
Example:
A company removed an
outdated series of v-belts from
their catalog after the manufacturer discontinued
production. This action prevented the purchase of
obsolete parts and helped avoid maintenance delays
caused by incompatible components.
Key Challenges in MRO Cataloging
- Common challenges include non-standardized data, data silos, and resistance to adopting new cataloging processes.
-
Data Accuracy and Consistency
- Inconsistent Item Descriptions: Variations in descriptions, part numbers, and specifications from different suppliers often cause confusion and procurement errors.
- Duplicate Entries: Difficulty identifying and consolidating duplicates can lead to overstocking and ordering mistakes.
-
Integration Across Systems
- Data Silos: Challenges in integrating MRO catalog data with systems like ERP, inventory, and maintenance platforms result in inconsistent data visibility.
- Lack of Real-time Synchronization: Delays in updating inventory and catalog information may cause stockouts or excess inventory.
-
Supplier Management
- Diverse Supplier Data Formats: Managing product data from multiple suppliers, especially with inconsistent item descriptions, adds complexity.
- Vendor Communication Issues: Insufficient communication regarding updates or discrepancies can disrupt catalog accuracy.
-
Maintenance and Replacement Management
- Complex Lifecycle Tracking: Keeping track of item wear, maintenance schedules, and replacements is challenging.
- Inadequate Preventive Maintenance Planning: Poor planning leads to unexpected downtime and higher maintenance costs.
-
Cost Control and Budgeting
- Balancing Procurement Costs: Finding the right balance between stocking enough items and avoiding excessive inventory costs can be difficult.
- Managing Vendor Pricing: Price variability and lack of negotiation strategies add to procurement challenges.
-
User Training and Adoption
- User Resistance: Stakeholders may resist using the catalog effectively due to insufficient training or lack of motivation.
- Continuous Training Needs: Ongoing education is required to keep users updated on catalog changes, new features, and best practices.
-
Data Quality Control
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Data: Missing or outdated information can lead to errors in procurement.
- Validation Processes: Strong validation measures are necessary to maintain data consistency and quality.
-
Maintenance of Historical Data
- Tracking Changes Over Time: Maintaining accurate records of catalog changes is essential for audits and compliance.
- Documenting Lifecycle Stages: Lack of systematic recording makes managing replacements and performance tracking difficult.
Example:
A company faced challenges because each department
used different naming conventions for parts. This
caused confusion and errors in part selection,
delaying maintenance work. The issue was resolved by
implementing a standardized cataloging system.
Best Practices
Effective MRO cataloging is supported by the following best practices:
-
Prioritize High-Value Items: Begin by focusing on critical equipment and essential parts.
-
Conduct Pilot Projects: Test cataloging methods on a smaller scale before rolling them out broadly.
-
Scale Incrementally: Expand the catalog gradually to prevent overloading systems and teams.
-
Integrate with ERP Systems: Ensure seamless connection between the MRO catalog and ERP for real-time data updates.
-
Maintain Data Quality: Regularly clean the data to eliminate duplicates and outdated entries.
-
Encourage Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Use user feedback, performance insights, and compliance checks to keep the catalog current and effective.
Example:
One company began by cataloging frequently used
items such as filters and bearings before gradually
including less critical parts. This strategy allowed
them to refine their process before scaling it
across the entire MRO inventory.
Data Visualization Tools
Visualization tools such as dashboards offer real-time insights into MRO data health, inventory levels, and usage trends.
-
Dashboard Tools
- Real-time Analytics Dashboard: Displays live key metrics including stock levels, usage patterns, and compliance status.
- Customizable Widgets: Allows users to tailor widgets for tracking specific data like maintenance schedules, part replacements, and compliance deadlines.
-
Heatmaps
- Stock Heatmaps: Color-coded maps showing inventory by location, enabling quick identification of overstocked or low-stock items.
- Usage Heatmaps: Visualize frequency of item use to support proactive maintenance and inventory control.
-
Trend Lines and Charts
- Usage Trend Charts: Illustrate historical usage to forecast demand and adjust inventory accordingly.
- Compliance Trends: Track regulatory changes over time to ensure ongoing compliance of catalog items.
-
Pie Charts and Bar Graphs
- Item Category Breakdown: Display the distribution of various item categories within the catalog.
- Supplier Contribution: Bar graphs showing each supplier’s product share, aiding in vendor evaluation.
-
Line Charts
- Lifecycle Management: Visualize maintenance schedules and replacement timelines to support proactive planning.
- Cost Over Time: Monitor expenses related to maintenance and replacements to optimize budgeting and procurement.
-
Bubble Charts
- Performance and Cost Analysis: Compare parts by performance and cost, with bubble size indicating relative importance.
- Risk Assessment: Represent operational risks from non-compliance or failures, with bubble size showing impact severity.
-
Visual Alerts
- Alert Threshold Indicators: Use color-coded alerts for stock, maintenance, and compliance deadlines to prompt timely action.
- Data Visual Notifications: Send notifications based on set thresholds like low stock or overdue maintenance.
-
Reports and Analytics
- Automated Reports: Generate regular summaries highlighting stock trends, maintenance schedules, and compliance status.
- Advanced Analytics Tools: Utilize predictive analytics to forecast maintenance needs and optimize inventory management.
Example:
A manufacturing facility used a dashboard to track
inventory and usage trends, helping to prevent stock
shortages and ensuring timely procurement and
maintenance activities.
Cost Optimization
Efficient MRO cataloging can drive substantial cost savings by minimizing duplicate purchases, streamlining procurement workflows, and preventing overstocking.
-
Demand Forecasting
- Historical Usage Data: Analyze past consumption patterns to predict demand, helping maintain optimal stock levels and avoid excess inventory.
- Seasonal Trends: Monitor seasonal fluctuations to fine-tune procurement strategies and reduce surplus during low-demand periods.
-
Supplier Collaboration
- Volume Discounts: Work with suppliers to secure better pricing through bulk purchase agreements for MRO items.
- Consignment Stock: Employ consignment arrangements to lower upfront costs by paying only for items when they are used.
-
Compliance and Regulatory Cost Control
- Monitor Compliance Requirements: Regularly verify that items meet regulatory standards to avoid fines and penalties.
- Risk Management: Detect non-compliant parts early using catalog data, enabling timely replacements or upgrades.
-
Cost-benefit Analysis
- Performance vs. Cost Analysis: Leverage catalog data to compare items or suppliers by balancing performance and costs.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate overall costs—including purchase price, maintenance, and compliance—to inform smarter procurement decisions.
-
Integration with ERP Systems
- Linking Catalog to Financial Data: Connect the MRO catalog to financial systems for improved expense tracking and cost management.
- Real-time Cost Tracking: Utilize ERP integrations to monitor procurement costs continuously, enabling agile purchasing strategies.
Example:
After implementing an optimized cataloging system, a
company reduced rush orders and excess inventory,
resulting in a 30% annual savings in MRO expenses.
Conclusion
Moresco is a reliable partner for MRO Cataloguing and Category Management, providing AI-driven solutions that enhance the management of materials, vendors, and services. Through tools like PureData and Assure, organizations can improve data accuracy, remove inefficiencies, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Supporting ERP transformations, inventory optimization, and continuous data governance, Moresco helps businesses streamline operations, cut costs, and make data-driven decisions. This robust master data management approach boosts efficiency across cataloguing and category management workflows.

